Introduction
Professor Douglas McGregor first explained the “Theory X and Theory Y” in his book ,”The Human Side of Entreprise” in 1960. Theory X and Theory Y presents the contrasting model of human behaviours and workforce motivation. This rise to two management style:
- Authoritarian (Theory X)
- Participative (Theory Y)
Both management styles reflect different human behaviours and approaches to motivation.
Theory X
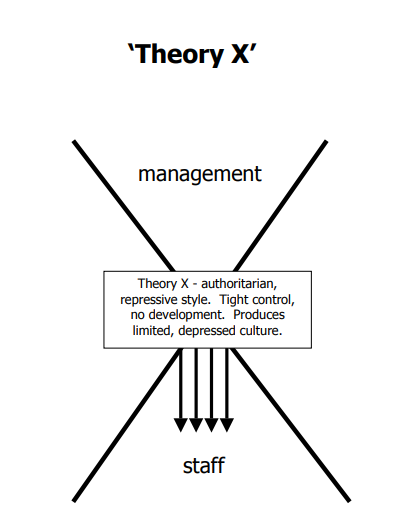
Individuals with Theory X characteristics consider a pessimistic view of their workforce and assume that employees are naturally unmotivated and dislike work. Therefore, Theory X encourages the use of tight control and supervision and follows a conventional approach to business. There are some of the assumptions for Theory X management ;
- Work is distasteful to most of people and they will try to avoid work whenever possible.
- People do not desire for responsibility and prefer direction from others.
- Most of the people do not opt for creativity in solving organizational problems.
- Psychological and Security needs to motivate people.
- People are not self-motivated and they require control and coerce to achieve organizational objectives.
- Most of people resist change.
Theory X has three proposition to define the conventional conception of management’s task:
- Management is responsible for organizing the elements of productive enterprise- money, materials, equipment, people- in the interest of economies ends.
- With respect to people, this is a process of directing their efforts, motivating them, controlling their actions, modifying their behaviour to fit the needs of the organization.
- Without this active intervention by management, people would be passive even resistant to organizational needs. They must therefore be persuaded, rewarded, punished, controlled- their activities must be directed . This is management’s task. We often sum it up by saying that management consists of getting things done through other people.
All these propositions, characteristics and assumptions suggest Theory X to be authoritarian. Such management style suggests that control is appropriate for dealing with unreliable, irresponsible and immature people. Such style will have high centralization of authority. This suggests that monetary return and job security are primary sources for employee motivation.
Theory Y

Theory Y individuals are more optimistic, concerned, positive, and open towards other people and individuals with such characteristics believe in a decentralized and participative approach to organizational function. Individuals consider the high-level needs of esteem and self-actualization are primary factors that best motivate employees. Theory Y individuals believe in continuous development and prefer participation over control. Theory Y relies heavily on self-control and self-direction.
There are some of the assumptions for Theory Y individuals are:
- The expenditure of physical and mental effort in work is as natural as play or rest.
- External control and the threat of punishment are not the only means for bringing about effort towards organizational objectives. Man will exercise self-direction and self-control in the service of objectives to which he is committed.
- Commitment to objectives is a function of the rewards associated with their achievement.
- The average human being learns, under proper condition.
Theory Y assumes that people are self-motivated, and thrive on responsibility. Management involves employees in decision making and implementing decisions. An appraisal is a regular and important strategy.


1 thought on “Theory X and Theory Y”