What is a Government Bond ?
A government bond is a debt instrument issued by the government to finance the spending and obligations of the government. Majority of the time, government bonds are issued with the purpose to finance government’s deficits.
Such bonds issued by the government are low risk investment as it is backed up by the government itself. Governments use such bonds to raise funds for new projects and infrastructures.
How does Government Bonds work ?
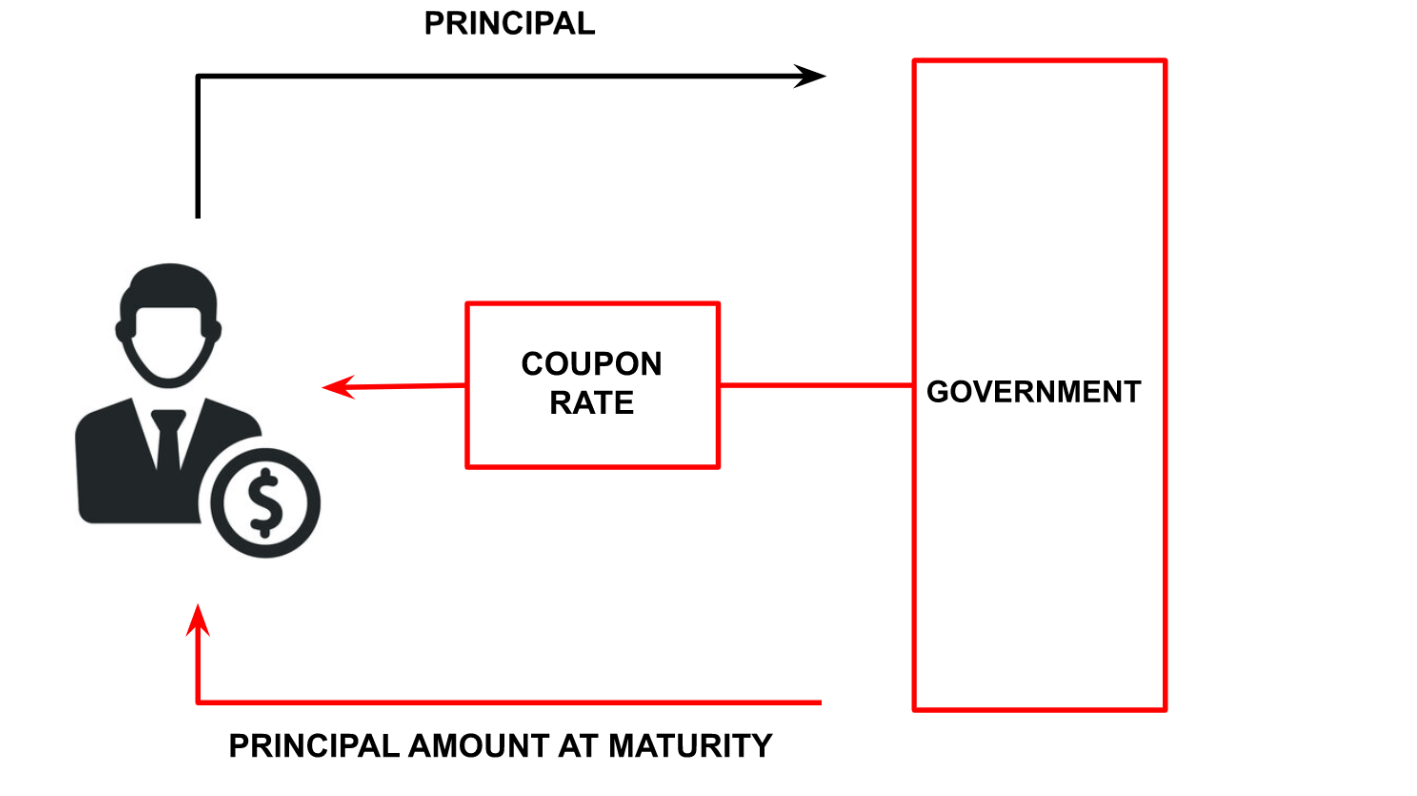
When the government requires to raise funds for a certain purpose, it announces government bonds. When any investors buy a government bond, that investor is lending an agreed amount of money (Principal) to the government for a defined period of time. For this lending, the government pays fixed interest at a regular time period as a coupon amount. At maturity or when the bond expires, investors receive the investment amount (principal).
The requirement of investors for government bonds is different based on the nature of the government bonds and regulation of the host country. Some countries allow individual investors to invest in government bonds and some countries only allow institutional investors.
What are the characteristics of Government Bonds ?
- Government bonds have high creditworthiness as it is backed by the government.
- Such bonds have low-to-no risk. Due to its backup, government bonds have low to no default risk.
- Government bonds have high liquidity. Due to the high creditworthiness and low-to-no risk, government bonds have a viable secondary market.
- Government bonds pay interest (coupon payments) on the investment. Interest rate in bonds varies as per the maturity period. Higher the maturity period, higher the interest rate.
- Such bonds can only be issued by the central government or state government or any other government authorities.
- Some special government bonds offer certain tax exemptions.
How are Government Bonds used ?
- Government bonds assist in funding government deficits.
- Such government debt issuances assist to fund daily operations.
- Government uses bonds to raise capital for various infrastructure spending.
- Sometimes government bonds are used to control the nation’s money supply.
- For investors, government bonds are used as collateral when taking loans.
What are the types of Government Bonds?
Government issues bonds for different purposes. Different countries have different requirements for raising bonds. Developed economies have a rich bond market and interested investors for bonds, hence the nature of bonds in developed countries may be different from nature of bonds in developing or under developing economics. Some of the common types of government bonds across economies are:
| Government Bonds (U.S.) | Government Bonds (U.K.) | Government Bonds (India) |
| U.S. Treasury Securities | Conventional Gilts | Sovereign Gold Bonds |
| Municipal Bonds | Index-linked Gilts | Sovereign Guarantee Bonds |
| U.S. Savings Bonds | Perpetual Gilts | Inflation Indexed Bonds |
| Mortgage Backed Bonds | Fixed Rate Bonds | |
| Corporate Bonds | Government of India Saving Bonds | |
| TIPS and STRIPS | Floating Rate Bonds | |
| Agency Securities | Bonds with Call or Put Options | |
| International and Emerging Market Bonds | Zero-coupon bonds |
Reference

