Introduction to Corporate Restructuring
Corporate Restructuring is a strategic decision. It is an action taken by a corporate to significantly modify the financial and operational aspects of the company, usually when the business is facing financial stress. Also, Corporate Restructuring can also be considered as the process of changing the business operations and business portfolio in order to assess more profitable business options. In corporate restructuring, there are either operational or functional structure changes or changes in the business model of the company.
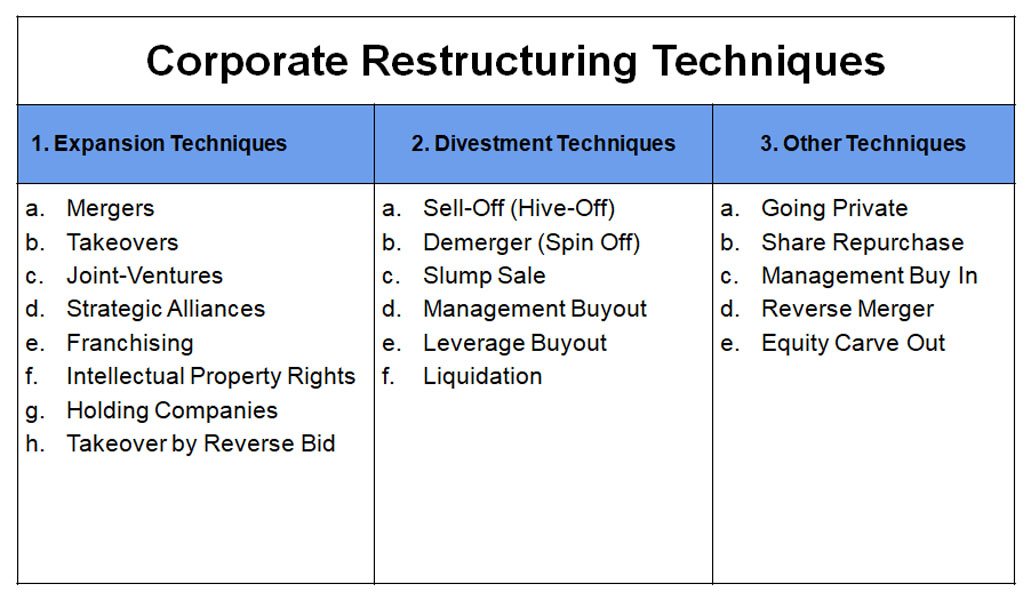
There are several restructuring techniques which are generally adopted in the corporate environment. All those restructuring approaches can be categorized into three broad types:

Expansion Strategies
Mergers
A merger is fundamentally the combination of two or more business entities in which only one entity remains. It is voluntary fusion of two or more companies on broadly equal terms into a new legal entity. The firms participating in the merger are typically similar in size i.e. customer base, scale of operation, market size etc. Mergers are most commonly done to gain market share, reduce costs of operations, expand to new territories, unite common products, grow revenues, and increase profit. After a merger, shares of the new company are distributed to existing shareholders of both original businesses. Some of the examples of Mergers are:
- Exxon and Mobil : Merger Deal $ 81 Billion
- AOL and Time Warner: Merger Deal $ 164 Billion
- Vodafone and Mannesmann: Merger Deal $ 180.95 Billion
- AT & T and BellSouth: Merger Deal $ 86 Billion
Reasons for Mergers:
- Growth
- Synergy
- Diversification
- Increase in Value
- Economies of Scale
- Economic Necessity
- Operating Economies
- Utilization of tax shields
- Better Financial Planning
- Eliminations of Competition
Takeovers/Acquisitions
Acquisition also known as takeover is a corporate restructuring technique where one entity is consumed or ceases to exist. In an acquisition, a larger company takes over all of the operational management decisions of a comparatively smaller company. In economic terms, when a financially able company acquires more than % of shares to take over another company. Acquisition can be friendly and hostile and the acquired company gets dissolved.
Some of the examples of Acquisitions:
- Walt Disney acquired Marvel Entertainment for $4 Billion.
- Google acquired Android for $50 Million.
- IBM acquired Red Hat for $34 Billion.
- Adobe acquired Marketo for $4.75 Billion.
- JAB Holdings acquired Panera for $7.5 Billion.
- Facebook acquired WhatsApp for $19 Billion.
- Tata Motors acquired Jaguar Land Rover for $2.3 Billion.
Reasons for Acquisitions:
- Growth
- Taxation
- Access to funds
- Risk diversification
- Entry to new markets
- Business diversification
- Synergistic operating economics
Joint-Ventures
A joint venture is a new enterprise owned or formed by two or more business entities for a special purpose for a limited duration. In this form of business formation, venture partners continue to exist as a separate form and the joint-venture represents a new business enterprise. Joint- venture can be considered as a contract to work together for a period of time to fulfill a certain strategic objective. The main purpose of Joint Venture is to limit the risk.
Some of the famous Joint-Ventures are:
- Volvo and Uber $300 million Joint-Venture to develop self-driving cars.
- Toyota and Mazda Joint-Venture in building manufacturing plants.
- Ford and Volkswagen Joint-Venture to develop self-driving and electric cars.
- Kellogg Company and Wilmar International Limited Joint-Venture to manufacture and sell cereal and other snacks in China.
Reasons for
Joint-Venture
- Synergy
- Diversification
- Shared resources
- Economies of Scale
- Access to new markets
- Strategic for competition
- Sharing & Spreading costs
- Economic Necessity
Strategic Alliances
Strategic Alliance implies an agreement between two or more entities to work jointly with one another to increase the performance of the participating entities. Strategic alliance may or may not include any contract. Strategic Alliance is more a form of collaboration or corporate partnering and hence there are no separate legal entities unlike Joint-Venture. The main objective of Strategic Alliance is to maximize the reward. Considerably, strategic alliances include product, knowledge, expertise, goodwill, capital etc.
Some of the example of strategic alliances are:
- Alliance between Spotify and Uber to increase the customer base as they offer Uber riders to take control of the stereo.
- Alliance between Apple and Mastercard to provide Apple Pay’s services.
- Alliance between Sony and Panasonic to produce a new generation TV.
Reasons for
Strategic Alliance
- Economies of scale
- Setting new standards
- Overcoming competition
- Enhancing competitiveness
- Sharing global business risks
- Exploring new foreign markets
- Acquiring new skills and resources
- Promoting innovation and technology
Challenges in Strategic Alliance
- Choosing the right partner
- Upholding Trust and Honesty
- Misrepresentation in alliance and resources
Holding Company
Holding Company is a parent company which owns enough voting rights in another company (subsidiary) and controls the policies and oversees the management decision. Parent corporations can control the policies of subsidiaries and oversee management decisions but don’t involve in regular routine operations. Holding company structure is one of the corporate structure techniques as holding companies take tax and liability benefits from the subsidiary companies.
Some of the examples of holding companies
- In 2015, Google underwent a corporate restructuring and was re-organized as a subsidiary of Alphabet, Inc.
- Sony Corporation holds major subsidiaries such as Sony Electronics inc., Sony Global Manufacturing & Operations Corporation, Sony Interactive Entertainment Inc., Sony Music Entertainment, Sony Pictures Entertainment etc.
- JP Morgan Chase & Co. has over 40 subsidiaries and some of the significant subsidiaries are JP Morgan Chase Bank, JP Morgan Asset Management holdings Inc., JP Morgan Securities LLC and Chase Bank USA.
- Johnson & Johnson has over 260 operating subsidiaries across the globe and some of the subsidiaries are Cordis Corporations, Ethicon, Inc., Janssen Biotech, Inc., Johnson & Johnson Pharmaceutical Services, McNeil Consumer Health etc.
Advantages of a Holding Company:
- Tax consolidation benefits
- Reduction of business risks
- Easier to form a holding company
- Diversity within the business world
- Reduces the legal risks of the involved entities
Corporate restructuring: Definition concepts and reasons
References