Introduction: Product Life Cycle
A product life cycle is the period of time from when it is initially made available to customers until it is discontinued. Management and marketing professionals use this idea as a decision element when determining whether it is suitable to enhance advertising, lower prices, enter new markets, or change packaging.
A product first starts as a concept, and under the constraints of contemporary business, it is unlikely to advance until it has undergone research and testing and is considered practical and potentially profitable. The product is then created, advertised, and launched. Although the product has not yet been introduced to customers, some product life cycle models involve product development as a stage.
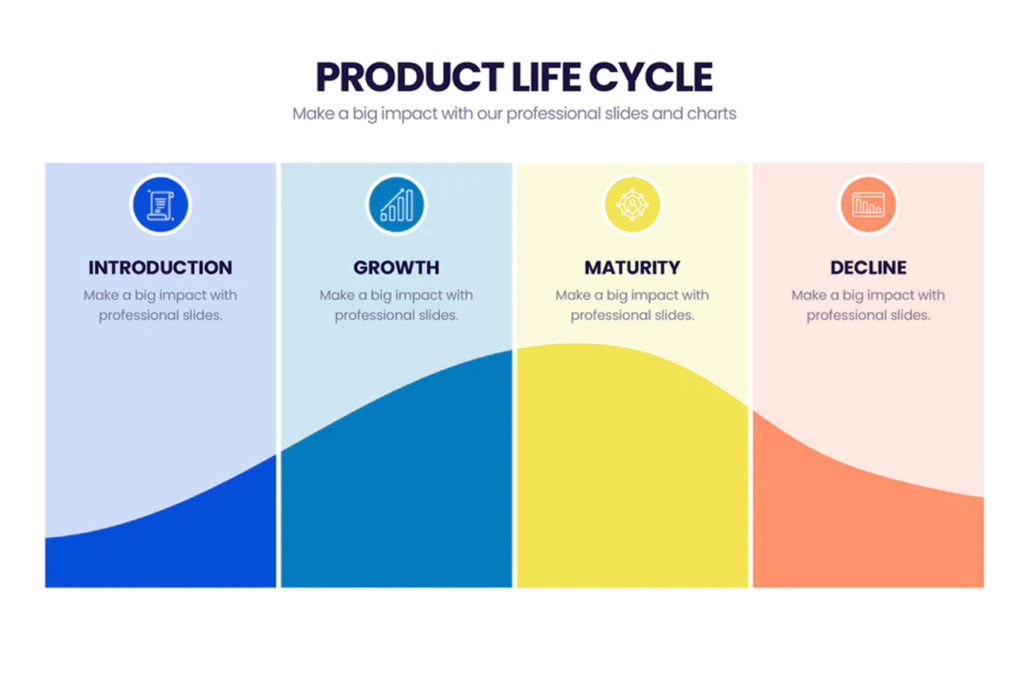
Stages in Product Life Cycle
Generally, the life cycle of a product can be divided into four stages: introduction, growth, maturity, and decline.
Introduction Stage
Since other rivals may be getting an early look at competing items, there is frequently minimal to no competitiveness for a product during the introduction period. However, as sales are typically lower at this point, there may not be enough special pricing to encourage customer participation, and the sales approach is still being scrutinized, businesses still frequently have poor financial outcomes.
Characteristics of Introduction Stage of The Product Life Cycle
- Sales growth is minimal and slow.
- Market pioneers or early adapters but the products.
- The capacity of production is low, hence, low to no economies of scale.
- The prices for goods and services are higher
- There is negative to no profit due to high costs and slow growth in sales.
- Frequent operational challenges
- For introductory products, there is very little competition as the viability of the product- is unknown.
Growth Stage
Based on its success, the product enters the growth stage where it is characterized by a rise in demand, supply expansion, and rise in production. The product gains in popularity and recognition throughout the growth phase. If a product is subject to intense competition, a corporation may nonetheless decide to invest extensively in advertising. However, marketing strategies will probably focus more on how to set their product apart from competitors than on how to get their products on the market. Based on client input, a business may potentially improve the functioning of a product.
Characteristics of Growth Stage of Product Life Cycle
- There is a rapid increase in sales of the product or sales.
- Product is tested in the market hence, there is more demand and buyers for the products.
- Prices are relatively stable and more efforts are made for promotion and marketing.
- Profitis slowly increased due to high sales turnover and low cost of production.
- Product or services are revised to its optimum and operational inefficiencies are managed.
Maturity Stage
The most lucrative stage of a product’s life cycle is when it reaches maturity, while production and marketing expenses are in the fall. Competition is at its peak during the mature stage. Competition for clients is typically at its strongest since rival businesses have had enough time to launch competing and improved products. A corporation aims to keep its product in this maturity phase for as long as feasible as sales levels steady.
Characteristics of Maturity Stage of the Product Life Cycle
- Competition is at its peak at maturity stage. There are many similar and substitute products.
- The sales growth rate is slowly decreasing due to competition and product saturation.
- Prices are competitive due to competition and economies of scale.
- Slower growth rate leads to lower revenue and eventually lower profits.
- Promotion is heavy to attract the new buyer group.
Decline Stage
The product can lose market shares and start to deteriorate as competition rises as other businesses try to replicate its success. Because of market saturation and competition from alternative items, product sales start to fall, and the company may decide not to pursue further marketing initiatives since consumers may already have made up their minds about whether or not they are devoted to the company’s products.
Characteristics of Decline Stage of the Product Life Cycle
- In the decline stage, businesses limit product and service offering. At this stage, businesses decide whether to discontinue the product.
- There is a dip in the business leading to low sales, revenue and profit.
- Competition in the business decreases in this stage.
- Customers are saturated and are in no state to purchase the existing product.
An Illustration to Product Life Cycle : Nokia
To have a better understanding about the concept of product life cycle, we’re going to elaborate it with the story of Nokia mobile phone. The rise and fall of the Nokia Phone in the Mobile Phone industry. Fredrik Idestam founded Nokia, a multinational corporation with headquarters in Finland, in 1865.
With respect to the introduction stage, Nokia introduced the Nokia 1011 Digi-handheld GSM phone in 1992. Due to the low level of demand and sales, it didn’t offer or launch a wide range of models. Nokia offered both GSM and CDMA mobile devices. During this stage, Nokia established themselves as a brand for manufacturing mobile devices.
This was followed up by the release of the Nokia 3210, their first cellphone without an antenna, in 1999. During this period, Nokia was one of the best brands in the cellphone industry. With sales of more than 160 million copies, this particular model became the most well-known and profitable phones of that time. Nokia then introduced phones like the N95 to challenge Samsung and the iPhone when they entered the market.
During the maturity stage, Nokia introduced many touch screen models. The N-97 qwerty plus touch model enjoyed the greatest success and earned the most profits. However, the company made a number of errors in their product modification during this phase which eventually saw their decline in the market.
Nokia’s collapse was caused by its subpar product design and preoccupation with Windows as its operating system. Nokia is now going through this phase. As of now, the company has relaunched itself as a budget friendly brand. Although they have a variety of phones launched in the market, they’ve retargeted themselves among the lower and middle class consumers.
References